Introduction
Stock trading can be a complex and challenging endeavor, requiring investors to navigate through a sea of market fluctuations and uncertainties. However, there are powerful tools and concepts that can assist traders in making informed decisions. In this blog post, we will explore two key concepts that can significantly enhance stock trading strategies: standard deviation and mean reversion.
Standard deviation is a fundamental measure of volatility and risk in stock prices. By analyzing standard deviation, traders can gain insights into the price movements and potential risks associated with specific stocks. It provides a quantifiable metric to gauge the magnitude of price fluctuations and assess the likelihood of future price changes.
Mean reversion, on the other hand, is a trading strategy that operates on the belief that stock prices tend to oscillate around their average or mean value over time. By identifying instances where prices deviate significantly from their mean, traders can potentially capitalize on market inefficiencies. Mean reversion allows traders to spot overbought or oversold stocks, suggesting potential opportunities for profit when prices eventually revert back to their mean.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into these concepts and demonstrate how traders can combine standard deviation and mean reversion to develop effective trading strategies. By leveraging the information provided by standard deviation and using mean reversion principles to guide entry and exit points, traders can improve their decision-making process and increase their chances of success. We’ll also provide practical examples and tips for implementing a trading strategy that incorporates standard deviation and mean reversion. By the end, you will have a solid foundation to explore these concepts further and potentially enhance your own stock trading approach. So, let’s dive in and uncover the power of standard deviation and mean reversion in the world of stock trading.
Understanding Standard Deviation in Stock Trading
Standard deviation plays a crucial role in stock trading as it provides valuable insights into the volatility and risk associated with stock prices. By understanding standard deviation, traders can make more informed decisions and assess potential trading opportunities. Let’s explore this concept further:
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that quantifies the dispersion of a dataset from its mean. In finance, it is commonly used to measure the volatility or variability of stock prices. A higher standard deviation indicates greater price fluctuations, indicating higher risk, while a lower standard deviation suggests relatively stable price movements. By calculating the standard deviation of historical stock prices, traders can gain insights into the level of volatility a stock exhibits. Volatile stocks with higher standard deviations tend to experience larger price swings, making them riskier investments. On the other hand, stocks with lower standard deviations are considered less volatile and may appeal to investors seeking stability.
Let’s consider two hypothetical stocks, Stock A and Stock B. Stock A has a standard deviation of 5%, while Stock B has a standard deviation of 20%. This indicates that Stock B exhibits higher price volatility compared to Stock A. Traders can use this information to assess their risk tolerance and make decisions accordingly.
Standard deviation can help traders identify potential trading opportunities by highlighting stocks with abnormal price movements. When a stock’s price deviates significantly from its historical standard deviation, it may indicate an overbought or oversold condition, suggesting a potential reversal in price. By monitoring standard deviation levels, traders can identify potential entry or exit points for their trades. Understanding standard deviation empowers traders to assess the risk associated with different stocks and make informed decisions. By incorporating standard deviation analysis into their trading strategies, traders can gauge market volatility and identify potential opportunities to capitalize on price movements. In the next section, we will explore mean reversion, another powerful concept that complements standard deviation in stock trading.
Mean Reversion: A Powerful Trading Strategy
Mean reversion is a trading strategy that capitalizes on the belief that stock prices tend to oscillate around their average or mean value over time. This concept is widely used by traders to identify opportunities when prices deviate significantly from their mean. Let’s delve deeper into mean reversion and its application in stock trading:
Mean reversion is the idea that stock prices, after experiencing significant deviations from their mean, are likely to revert back to their average value. This occurs due to the forces of supply and demand, as well as market participants’ reactions to price extremes. Mean reversion traders aim to profit by taking positions when prices are expected to revert to their mean.
Stock prices rarely move in a straight line. Instead, they exhibit a tendency to fluctuate above and below their average value. Mean reversion traders identify these price swings and take advantage of the potential reversals when prices move too far away from their mean. They anticipate that the price will eventually return to a more reasonable level.
Mean reversion allows traders to identify overbought and oversold conditions in stocks. When a stock’s price significantly exceeds its historical average, it may be considered overbought, indicating a potential opportunity to sell or short the stock. Conversely, when a stock’s price falls significantly below its mean, it may be considered oversold, suggesting a potential opportunity to buy or go long on the stock.
Numerous successful trading strategies are based on mean reversion. For example, the “Pairs Trading” strategy involves identifying two stocks that are historically correlated. When one stock’s price significantly deviates from its normal relationship with the other stock, traders can take positions anticipating a reversion to the mean relationship.
Mean reversion offers traders a powerful approach to identify potential trading opportunities. By understanding the tendency of stock prices to oscillate around their mean, traders can anticipate reversals and take advantage of price extremes. However, it is important to note that mean reversion strategies require careful analysis, risk management, and consideration of other market factors.
In the next section, we will explore how standard deviation and mean reversion can be combined to create a robust trading strategy. By integrating these two concepts, traders can enhance their decision-making process and potentially increase their chances of success in the stock market.
Combining Standard Deviation and Mean Reversion for Trading
The combination of standard deviation and mean reversion can provide traders with a powerful framework for identifying potential trading opportunities and improving their overall trading strategy. Let’s explore how these two concepts can be effectively merged:
Standard deviation can assist traders in identifying optimal entry and exit points for their trades. By considering a stock’s current price in relation to its historical standard deviation, traders can gauge whether the stock is trading at an extreme level. If the price deviates significantly from the mean, it may present an opportunity to enter a trade with the expectation of a mean reversion. By combining standard deviation and mean reversion, traders can uncover potential trading opportunities that align with their risk tolerance and strategy. When a stock’s price exhibits a significant deviation from its mean, and this deviation is also accompanied by a high standard deviation, it strengthens the case for a potential mean reversion trade.

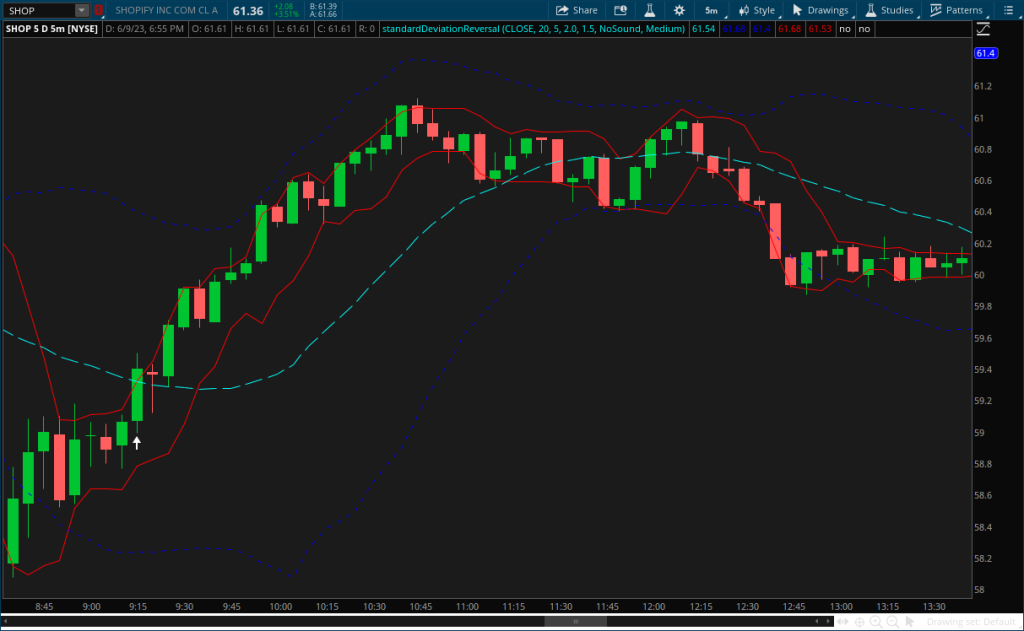
Standard Deviation Reversal Indicator for Thinkorswim
Standard deviation is the statistical measure of market volatility, measuring how widely prices are dispersed from the average price. Standard deviation is commonly used as a risk indicator and volatility measure. The standard deviation reversal indicator for thinkorswim is used in mean reversion strategies, and displays visual signals with optional audible alerts to indicate when the short term channel trend moves against the long term channel trend. This indicator displays on all timeframes in the thinkorswim platform.
Traders can establish specific trading rules based on the combination of standard deviation and mean reversion. For example, they may decide to enter a trade when a stock’s price exceeds a certain number of standard deviations from its mean, indicating an overbought or oversold condition. Similarly, they may set rules for exiting a trade once the price approaches the mean or reaches a specific profit target. By integrating standard deviation and mean reversion, traders can enhance their trading strategies. This combination allows for a more comprehensive analysis of stock prices, incorporating both volatility and the tendency to revert to the mean.
In the next section, we will discuss the risks and limitations associated with using standard deviation and mean reversion, as well as the importance of implementing effective risk management techniques in trading.
Risks and Limitations
While standard deviation and mean reversion can be powerful tools in stock trading, it’s important to understand and address the risks and limitations associated with these concepts. Traders must approach their strategies with caution and implement effective risk management techniques. Let’s explore these considerations:
- Market unpredictability: Despite historical data analysis, future market conditions can deviate from historical patterns, leading to unexpected outcomes.
- Extended periods of deviation: Stocks may remain overbought or oversold for prolonged periods before reverting to their mean, resulting in potential losses if not managed appropriately.
- False signals: Standard deviation and mean reversion strategies are not foolproof and can generate false signals, leading to incorrect trading decisions.
- Implementing proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, is crucial to protect against excessive losses.
- Traders should determine their risk tolerance and establish appropriate risk-reward ratios for each trade to mitigate potential losses.
- Standard deviation and mean reversion are just two tools in a trader’s toolkit. They should be complemented by other technical and fundamental analysis to gain a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
- Traders should be aware that no single strategy guarantees success in all market conditions. Flexibility and adaptability are key in adjusting trading strategies based on evolving market conditions.
It is essential for traders to be aware of the risks and limitations associated with using standard deviation and mean reversion in stock trading. By acknowledging these factors, traders can take a proactive approach to mitigate risks, manage losses, and refine their strategies accordingly.
In the next section, we will provide some valuable tips and best practices to effectively incorporate standard deviation and mean reversion into stock trading strategies, maximizing the chances of success while minimizing potential risks.
Tips and Best Practices
Incorporating standard deviation and mean reversion into stock trading strategies requires careful consideration and implementation. To help traders effectively utilize these concepts, here are some valuable tips and best practices:
Understand the historical price behavior of stocks, analyze standard deviation levels, and identify mean reversion opportunities. Supplement standard deviation and mean reversion analysis with other technical indicators and fundamental analysis to confirm potential trading signals. Analyze standard deviation and mean reversion across different timeframes to gain a broader perspective and validate potential trading opportunities.
Continuously monitor market news, economic indicators, and company-specific developments to stay abreast of any factors that may impact stock prices. Adjust trading strategies as market conditions evolve. Market trends and dynamics can shift, requiring traders to adapt their approach accordingly.
Use historical data to simulate and test your trading strategy based on standard deviation and mean reversion. Assess its performance under various market conditions to gain insights into its strengths and weaknesses. Monitor the results of your trades and continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your strategy. Identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to enhance performance.
Implementing these tips and best practices can help traders optimize their strategies and increase their chances of success when incorporating standard deviation and mean reversion. However, it’s important to remember that trading involves inherent risks, and no strategy guarantees profits. Prudent risk management and continuous evaluation of the strategy’s performance are key elements for long-term success.
In the concluding section, we will recap the key points discussed throughout the blog post and emphasize the potential benefits of utilizing standard deviation and mean reversion in stock trading strategies.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the powerful concepts of standard deviation and mean reversion in stock trading. By understanding and incorporating these concepts into trading strategies, traders can enhance their decision-making process and potentially increase their chances of success. Let’s recap the key points discussed and emphasize the benefits of utilizing standard deviation and mean reversion:
- Standard deviation serves as a measure of volatility and risk in stock prices. By analyzing standard deviation, traders can assess the magnitude of price fluctuations and identify potential trading opportunities.
- Mean reversion is a trading strategy that takes advantage of the tendency of stock prices to revert back to their mean value over time. By identifying price deviations from the mean, traders can anticipate potential reversals and capitalize on price extremes.
- Combining standard deviation and mean reversion allows traders to enhance their trading strategies. By utilizing standard deviation to determine entry and exit points and incorporating mean reversion principles, traders can identify overbought and oversold conditions and make more informed trading decisions.
- It is important to recognize the risks and limitations associated with these concepts. Market unpredictability, extended periods of deviation, and false signals can pose challenges. Implementing effective risk management techniques and considering additional analysis can help mitigate these risks.
- Practical tips such as thorough research, using multiple indicators, staying informed about market trends, and evaluating strategy performance through backtesting are essential for successful implementation.
By incorporating these concepts and following best practices, traders can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, improve their trading strategies, and potentially increase their profitability.
So, as you embark on your stock trading journey, consider the power of standard deviation and mean reversion. Explore, experiment, and develop your own unique trading approach. With the right knowledge, strategy, and risk management, you can navigate the stock market with confidence and aim for success.
As always, good luck and happy trading!